Thread Life Cycle in Java tells the various information of thread form born to terminate.
Thread life cycle contains the several stages and at a time any thread can be present in a single state.
States of Thread life cycle
- Born
- Ready
- Running
- Blocked
- Sleep
- Wait
- Dead
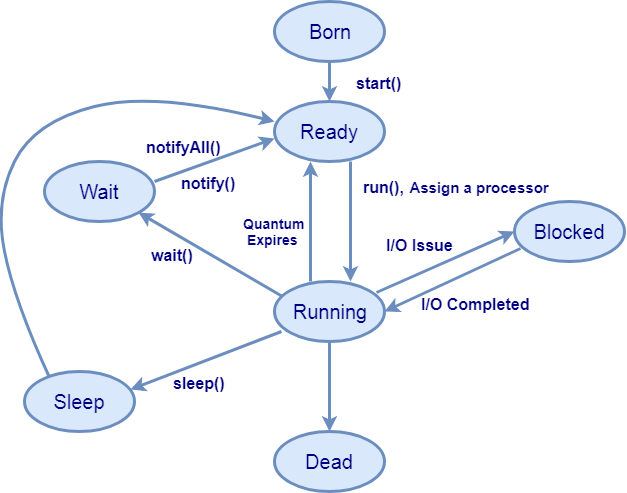
Ready: In this state thread is ready to execute but not running.
When the start() method calls thread enters from born to ready state.
Running: When a run() method executes highest priority ready thread assigned a processor and enter in a running state for execution.
Thread can visit more than ones in a running state.
Blocked: When a running thread has a input-output issue it enters in a blocked state from running state and when input-output issue solves it again comes in a running thread.
When sleep time expires then thread moves to ready state.
When a high priority thread execution completes it calls
Dead: A running thread is enter in a dead state when its execution completes (run() method completes) or terminate for any reason.
Multithreading in java example programs
- Created a class Thread1 that extends Thread class
- main() creates two thread t1 and t2.
- To start thread start method is called
t1.start()andt2.start() - Start method calls the run method to execute the work
Thread.sleep()send thread to sleep state for 500 milliseconds- From sleep state thread come back to ready then running state
- After completing work thread get dead.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | class Thread1 extends Thread { public void run() { try { for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("Running Thread: " + i); Thread.sleep(500); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("InterruptedException "); } } } public class TreadExample { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread1 t1 = new Thread1(); t1.start(); Thread1 t2 = new Thread1(); t2.start(); } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | Running Thread: 1 Running Thread: 1 Running Thread: 2 Running Thread: 2 Running Thread: 3 Running Thread: 3 Running Thread: 4 Running Thread: 4 Running Thread: 5 Running Thread: 5 |
Read More
